
9 tips to go digital in the natural ingredients for cosmetics sector
Digitalisation, along with artificial intelligence (AI), is shaping supply chains and international trade more and more. These advances offer opportunities to improve almost every part of operational processes. This includes sales, sourcing, logistics, finance, quality control, processing, marketing and supply chain management. AI-driven digitalisation helps suppliers reach more markets, optimise efficiency and build stronger relationships with buyers. For exporters of natural ingredients for cosmetics, digital tools and technologies are essential to stay competitive in the European market. This study offers nine tips to help exporters use digitalisation and AI, improve their operations, meet market demands and grow their business.
Contents of this page
- What digitalisation can do for your business
- Use big data to improve resilience
- Use digital financial tools to overcome finance challenges
- Improve transparency with blockchain technology
- Use online resources and big data to learn and grow
- Use e-commerce platforms to find buyers and boost sales
- Improve efficiency with business and inventory management tools
- Unlock digital potential with AI-driven tools
- Get support from national and regional organisations to go digital
1. What digitalisation can do for your business
'Digitalisation' means integrating digital tools and technologies into various parts of a business. This transformation is reshaping the cosmetics industry, including its manufacturing processes and how they communicate with customers. For exporters of natural ingredients for cosmetics, digitalisation offers great opportunities to streamline operations, to improve customer experiences and to access new markets, particularly in Europe. To get these benefits, however, you must choose the right digital tools and understand how to use them.
The cosmetics industry is going through a fast, digital transformation in both manufacturing and consumer engagement. In manufacturing, technologies like AI-driven product development and automated quality control are improving efficiency and innovation. For example, AI tools are being used to identify new safe molecules for formulations. These molecules can improve product safety and effectiveness. The industry uses digital twins – virtual replicas of manufacturing processes – to optimise production lines. On the consumer side, virtual try-on tools and augmented reality (AR) apps are improving the shopping experience. One example is letting customers see how products like makeup or skincare will look and feel before purchasing.
Figure 1: Changing role of digital technologies in agriculture
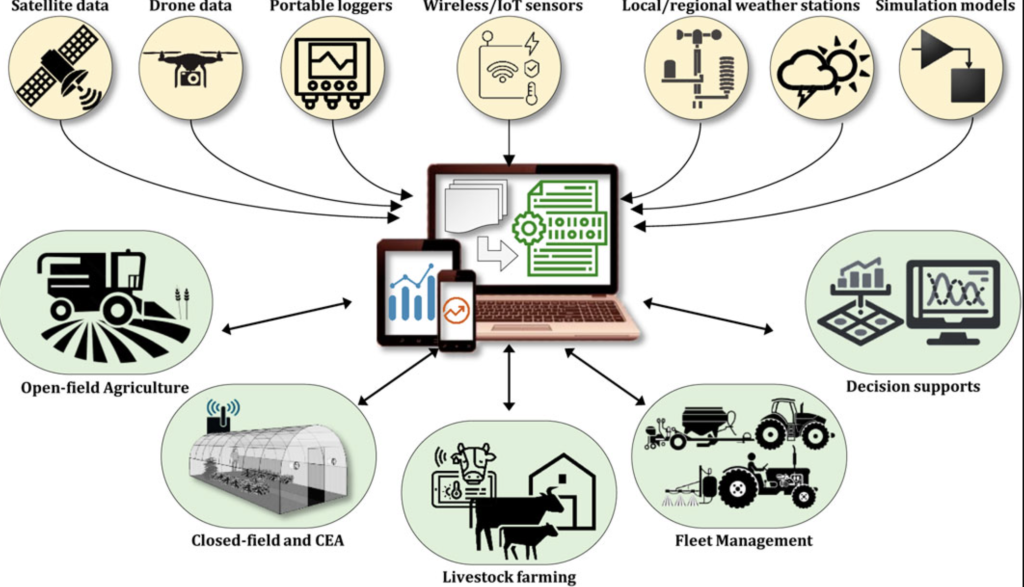
Source: Frontiers, 2024
Digitalisation can also help producers, aggregators and exporters. For producers, digital tools help improve farming practices, forecasting and monitoring, and can increase resilience to weather and climate change. This leads to better product quality and lower costs. For aggregators and exporters, digital tools can make operational processes, customer outreach, information management and financial transactions better. It also makes data sharing with clients and certification authorities more efficient.
There is a wide range of digital tools, each designed for specific functions within the supply chain. Understanding their uses and benefits is crucial.
- Digital agricultural tools. Technologies like precision farming and the internet of things (IoT) use data from drones and sensors to optimise fertilisation, irrigation and land use. These tools help farmers comply with regulations, such as reducing pesticide usage, and can also cut costs and increase productivity. For example, Cropin offers AI and IoT-based solutions to monitor crop health, manage resources efficiently and improve traceability throughout the supply chain.
- Post-harvest monitoring tools. Tools that monitor storage conditions, such as temperature and moisture, help preserve the quality of natural ingredients. These technologies are especially useful for processors handling sensitive cosmetic ingredients.
- Digital trade finance. Digital payment platforms enable secure and cash-free transactions for international trade.
- Online resources and big data. Data collected by organisations like Cosmetics Europe helps identify trends and market opportunities.
- Digital marketplaces and trade platforms. Online platforms connect suppliers with global cosmetic companies, and so open up new markets. These platforms are particularly useful for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). For ingredient suppliers: Producers Market (a global network of farmers, ingredient makers and buyers); Ingredients Online (natural ingredients and raw materials for the skincare and haircare markets); Knowde Marketplace (marketplace for ingredients, polymers and chemicals). For suppliers of finished products: Beautetrade (global B2B platform for cosmetics, with a very large buyer directory), The African Cosmetics Directory (lists wholesalers of cosmetics in more than 20 countries in Africa, and retailers of beauty products in more than 20 African markets).
- Business management and inventory management tools to improve efficiency.
- Blockchain technology. Improves traceability and transparency in the supply chain, makes real-time monitoring of product movements possible and securely encrypts important documents like contracts.
- Artificial intelligence (AI). AI-driven tools support demand forecasting, quality control and supply chain management. This helps suppliers to optimise production and reduce waste. AI can also support formulation development and analyse consumer trends.
Video 1: Three applications of AI in agriculture
Source: Conveniently Primed, 2021
Before starting to use digital tools, exporters must carefully look at their needs and goals. Digital transformation requires a lot of money and effort. A clear plan ensures success and avoids wasting resources.
Some key questions to ask yourself:
- What priorities and challenges can digital tools help with? Also, are there more important priorities you need to look at before going digital? And what type of digitalisation would be best for your situation and goals?
- What will you be able to earn back from the investment? Will the money you make be enough to pay for the costs of going digital?
- What about maintenance, training and unexpected costs? Can you manage the costs of adoption, maintenance and training? Do you have (or can you find) the people and the skills needed to make the most of digitalisation?
Digitalisation may be very useful for exporters of natural ingredients for cosmetics. For example, it can improve farming practices and traceability and help you find new markets. But success depends on choosing the right tools, based on a clear understanding of your business needs. You can only make the most of digitalisation and achieve long-term growth in the European market if you define your goals and choose solutions that actually help you achieve them.
Tips:
- Make a list of your needs before choosing or investing in any tool. What digital technology will work for you?
- Make sure that you have the skills and the people needed to make the most of digitalisation.
- Make sure you have the right mobile technology in place. You will need a smartphones or tablet for most digital solutions.
- Carefully choose the right level of digitalisation for your business and customers.
- Read the CBI study Tips for doing business with European buyers of natural cosmetic ingredients for more information about trading with Europe.
2. Use big data to improve resilience
Climate change and increasingly unpredictable weather are a real threat to the agriculture sector, and particularly for exporters of natural ingredients for cosmetics. SMEs in low and middle-income countries (LMICs) are especially vulnerable. That is why they need to develop strategies that respond effectively to these challenges. Big data gives you powerful tools that can help with this. With the right tools, you can build greater resilience and be successful in the competitive global marketplace.
Big data is the collection and analysis of large amounts of data, often generated by satellites, weather stations and crowdsourcing platforms. This data is analysed to predict future scenarios, identify trends and provide useful business information. In agriculture, big data is often used to understand weather patterns, soil health, pest and disease monitoring and market intelligence.
For businesses producing natural ingredients for cosmetics, specific big data solutions can improve both their resilience and profitability. For example, precise weather predictions and early warnings of extreme events let farmers plan their activities in advance. Platforms like Cropin deliver customised weather-based recommendations and information that help producers optimise how they farm and reduce risks.
In pest and disease management, data-driven tools analyse environmental factors to predict outbreaks. This makes pro-active management possible, which reduces crop losses. FarmStack by Digital Green, for example, sends real-time alerts about potential pest infestations. Big data can also keep an eye on inputs like fertilisers and water usage to help ensure compliance with European sustainability requirements. And tools like FarmBetter provide localised advice about eco-friendly practices, which again help exporters to comply with regulations.
Big data can optimise production and quality control, too. Analysing data about soil conditions, moisture levels and crop growth helps maximise yield quality and quantity. This is particularly important for natural ingredients requiring specific storage or processing conditions to maintain their effectiveness in cosmetic formulations.
The benefits of big data are clear. But starting to use these tools requires investment in technology, infrastructure and training. The costs vary depending on the platform and services you need. Tools like Cropin and FarmBetter have different price levels, which make them easy to use to small-scale producers. Government and non-profit initiatives often offer free or subsidised access to big-data resources such as climate data or pest monitoring systems. Subscription-based models such as FarmStack may cost more to begin with. But in the long term they can still save you money because they improve decision-making and efficiency.
To make the most of big data, you first need to look at the specific challenges you face: climate risks, pest outbreaks, market access and so on. Once you know what they are, you must choose solutions that are right for your company’s size, technical capacity and goals. You must also invest in training so that your personnel are able to use the tools effectively. After that, regular monitoring and evaluation will help you to keep refining your strategies and get better results.
Tip:
- Read the FAO publication E-agriculture in Action: Big Data for Agriculture to learn more about big data and its benefits for agriculture, including case studies.
3. Use digital financial tools to overcome finance challenges
Access to finance remains a big barrier for many producers of natural ingredients for cosmetics. A lack of financial resources makes it harder to invest in better inputs, technology and services. And that can affect yields and product quality, making it harder to meet the strict requirements set by European buyers. Digital financial services (DFS) are bridging this gap more and more, offering businesses the tools they need to access a full range of financial products.
DFS are especially useful in regions where there is not much traditional banking. By using digital channels instead, such as mobile phones and apps, they give smallholders, co-operatives and exporters access to credit, saving facilities, insurance and seamless payment systems. Tools like mobile banking, e-wallets and blockchain-based finance improve financial inclusion. This makes it easier for producers to access working capital, invest in certification programmes and grow their business.
Digital financial tools are making life much easier for many producers and exporters in the natural ingredients sector. Agri-Wallet, for example, offers digital wallets linked to credit and input financing. These let farmers and aggregators access credit based on their trading history. That is particularly interesting for farmers who supply shea butter, baobab oil and essential oils. Farmerline offers mobile-based financial services and working capital loans for cocoa, shea butter and moringa producers. And it also offers financial education to improve decision-making by smallholders. Another example, in Indonesia, is Julo: a mobile microfinance platform that offers low-interest digital loans for farmers and SMEs. This tool may be interesting for essential oil distillers who want to modernise their extraction processes.
Looking at mobile-based payments and trade finance, M-Pesa (in Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, DRC, India) is a mobile money platform that helps with cashless transactions between ingredient producers and buyers. It is widely used in vanilla, coffee and spice supply chains to process secure and traceable payments. At the global level, Wise and Payoneer make fast, low-cost international transactions possible. This helps exporters of natural ingredients to receive payments from European buyers without high banking costs. KiuPay, originally from Vietnam, offers digital payments and supply chain financing for smallholders growing ingredients such as turmeric, ginger and coconut.
Blockchain technology is changing trade financing by improving transparency and reducing fraud risks. Komgo, operating in Africa and Asia, offers a blockchain-based trade finance platform that helps exporters of natural ingredients to get financing from global banks. By digitalising trade transactions and improving security, Komgo helps businesses access working capital more efficiently. IBM Food Trust is another example that is used around the world, including in Africa. It uses blockchain to create more trust and traceability within supply chains. It offers secure digital records that exporters can use for creditworthiness assessments. It makes financial transactions smoother and more reliable.
To make the most of DFS, financial literacy is essential. Mosabi, for example, is active in West Africa, Latin America and Southeast Asia. It combines financial education with AI-driven alternative credit scoring. This helps farmers and ingredient processors access credit based on their mobile transaction history rather than regular banking. This approach improves financial inclusion, so that more producers can get the funding they need for their businesses. Likewise, Kisan Diary, used widely in India and Southeast Asia, helps farmers to manage their income, expenses and profitability by crop season. By providing digital financial tracking tools, it too supports better financial planning and so helps to optimise investments and operational costs.
Video 2: Market access for smallholder farmers
Source: Farmerline, 2021
Tips:
- Make sure that your devices and apps are always updated to the latest versions. This keeps them secure and helps keep your business products safe.
- Use mobile-based financial services to make transactions easier and track payments digitally.
- If possible, work with agri-fintech providers that offer customised credit solutions for natural ingredient producers. Help your suppliers access financial services by digitalising their transactions and giving them access to their transaction history. Banks can then use this digital transaction history for credit scoring and offer financial services to farmers with good credit.
4. Improve transparency with blockchain technology
Transparency in the supply chain has become a critical requirement for businesses in the natural ingredients for cosmetics sector. European buyers and consumers are increasingly demanding traceability, sustainable practices and accountability from suppliers. Blockchain technology is being used more and more in the beauty supply chain, and it is changing the way businesses deal with customer expectations. By enabling real-time tracking, secure data sharing and proof of ethical practices, blockchain improves trust and efficiency across the supply chain.
Blockchain is a decentralised and secure digital record of transactions. It shows the order of transactions and makes them visible to different parties. It can spot changes and ensure data integrity. This makes it an ideal tool to improve traceability and accountability in the cosmetics industry. Thanks to blockchain, companies can manage supply chain transactions, trace ingredient origins, ensure authenticity and provide buyers with detailed sustainability data.
For example, blockchain can help brands to check that claims about organic or natural ingredients are true, track where raw materials come from and ensure compliance with environmental and social standards. This technology also helps to ensure compliance with regulations like the European Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive.
Several platforms and tools use blockchain to improve transparency and traceability in the natural ingredients sector:
- Bext 360. This platform uses blockchain to document ingredient purchases and movements in real time. It ensures that payments are made directly to harvesters through mobile banking. It attaches digital receipts to each transaction. Buyers can trace exactly where the ingredients come from and verify payments. This improves ethical sourcing practices.
- TraceX. This tool shows suppliers’ sustainability credentials, certifications and fair-trade practices to buyers. It helps companies show they comply with sustainability standards and offers clear visibility about their supply chain operations.
- Producers Trust. This platform and its StoryBird software collect and present sustainability data. In this way it helps companies to de-risk supply chains, meet reporting requirements and build customer trust through data-driven storytelling.
- Provenance. Helps brands to track and communicate product journeys from source to shelf. This helps to check claims like organic certification and lets businesses show their commitment to transparency.
Blockchain has several advantages for SMEs in the natural ingredients sector. Automating data tracking means fewer manual errors, accelerates transactions and so improves efficiency. It also improves transparency and trust by letting multiple parties access correct and verifiable data. This transparency builds credibility with buyers and consumers, particularly in markets where people find ethical sourcing is important. Also, its ability to prove compliance with sustainability standards and ethical practices can strengthen a company’s market position, especially with eco-conscious consumers. For younger generations in particular, environmental and social responsibility is more and more important. Blockchain is a great strategic tool for businesses that want to show they share these values.
But despite its benefits, the use of blockchain is still in its early stages in the cosmetics supply chain. To introduce it successfully, everyone in the chain – including farmers, processors and buyers – must work closely together. The starting costs can be high, too, and proper training is needed to make the most of its potential. As demand for transparency grows, however, blockchain and related tools are expected to be used more widely.
Tips:
- Read the CBI study on blockchain in Europe for a better understanding of what blockchain is.
- Read Beyond the Blockchain by Agriterra and E-Agriculture in Action: Blockchain For Agriculture by the FAO for inspiring examples of blockchain technology in action, including the opportunities and risks involved.
- Before deciding to start using it, get advice from experts or from companies that have already invested in blockchain technology to check that it is right for you.
5. Use online resources and big data to learn and grow
The internet has many resources for exporters of natural ingredients for cosmetics, such as information about better production practices, market trends, demand analysis and regulations. These tools can help you comply with European market standards, find new opportunities and be more competitive. Thanks to online data and training materials, you can make more informed decisions and adapt to market demands.
Exporters have access to a number of specialised tools that offer crucial market information and promote international trade. The International Trade Centre (ITC) operates three very useful platforms:
- Market Access Map. This tool delivers detailed information on tariffs, regulatory requirements and market entry conditions for specific products. Exporters can easily search by product type or country to understand the barriers and opportunities in particular markets. This map also offers quick, user-friendly access to essential data that helps businesses make sense of the complexities of international trade.
- Export Potential Map. By analysing trade data, this platform finds export opportunities based on market demand and supply capacities. Exporters can use it to find target markets, to assess potential competition and to develop strategies that optimise their export plans.
- Trade Map. This tool offers a detailed analysis of export performance, international demand and competitive markets. Trade Map covers 220 countries and 5300 products and presents data in graphs, tables and maps. This makes it a very useful resource for exporters looking to expand their market reach and better understand global trade flows.
Besides the ITC tools, other platforms and organisations also give exporters valuable information:
- FAOSTAT. Managed by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), FAOSTAT offers data on food and agriculture, including production, trade and market statistics. This information is crucial to understanding global demand and supply trends.
- Eurostat. As the statistical office of the European Union, Eurostat offers international trade data categorised by HS code. This helps exporters to analyse European markets in detail.
- Access2Markets. This European Commission portal offers trade statistics and information about regulations to help exporters deal with market requirements and find new opportunities.
Keeping up with market developments and consumer preferences is essential for exporters. Industry-specific digital magazines and newsletters like Cosmetics Business, Cosmetics Design Europe, Cosmetics and Toiletries and SPATE offer updates on trends, regulations and innovations in the cosmetics industry. Exporters can also make use of the websites of industry associations such as the European Federation for Essential Oils (EFEO), the European Federation for Cosmetic Ingredients (EFFCI). FairWild (a standards and knowledge centre), Natrue (the International Natural and Organic Cosmetics Association) and Cosmos (a certification authority). These organisations offer valuable information on regulatory updates, market trends and industry standards. Members of these associations are also often potential customers and partners for exporters.
Figure 2: AgroTutor Academy’s free online digital skills courses

Source: ICTforAg Learning Network
The internet also makes it easier to access to regulatory information. Platforms like EUR-Lex, the European Union’s legal database, offer great access to regulations, directives and standards. Exporters can use EUR-Lex to stay informed about legal requirements affecting their products and to make sure they comply with European market standards. Trade fairs such as In-Cosmetics, Vivaness and Biofach also have websites with useful information, like press releases and profiles of the companies that will be there. Although visiting trade fairs in person is still the best way to build business relationships, their online resources give you a starting point to better understand market dynamics.
Using the resources available on the internet can be incredibly useful for exporters. Accessing market data helps you to spot trends and new opportunities, so that you can make informed decisions and target markets effectively. By keeping track of evolving regulations and standards, you can make sure you comply and position yourself as a reliable partner in the global marketplace. By learning more about sustainable and ethical production practices, you can meet consumer demands and improve your market appeal. Building a strong online presence attracts buyers and partners, and data from reliable online resources can help you develop strategies that are well-informed and impactful. In short, the internet helps exporters to improve their operations and stay competitive in the global market.
Tips:
- Visit the ICTforAg website and watch videos from past conferences and sessions to learn more about digitalisation in agriculture.
- Use the ITC Trade Map video tutorials to learn how to do basic export market screening by analysing the size and openness of markets and trends since 2001.
- Use this Access2Markets tutorial to analyse internal and external European trade in your natural ingredients for cosmetics.
6. Use e-commerce platforms to find buyers and boost sales
E-commerce (also known as electronic commerce or internet commerce) means buying and selling goods and services through the internet. This includes sending money and data to complete transactions. For exporters in the natural ingredients sector, e-commerce can be a powerful marketing tool that helps increase visibility and connect with potential buyers. It may not always lead directly to bulk sales, but it still offers useful opportunities to access new markets and improve customer engagement.
The percentage of consumers who buy cosmetics on the internet continues to increase. This trend is particularly strong in Europe, where online sales will probably reach 30% of total cosmetics revenue in 2025. In countries like Poland (70%), Portugal (56%), Spain (53%) and France (49%), online cosmetic purchases are now higher than the worldwide average of 46%. Sales are also strong in other important markets such as Germany and the Netherlands. This growing internet marketplace offers interesting opportunities for both brands and ingredient suppliers.
Online marketplaces give suppliers direct market access. You can make the most of e-commerce by choosing the right platform, maintaining a strong online presence and making sure that you sell products that customers want. As an exporter, e-commerce lets you:
- Promote and advertise your products by building an online presence that improves brand recognition;
- Access new markets by connecting suppliers with new customers and expanding their existing network;
- Simplify your business operations thanks to online transactions;
- Connect and communicate with smaller buyers looking for smaller amounts of natural ingredients; and,
- Better understand your market by tracking trends and buyer demand with the help of platform data.
E-commerce platforms can be classified into two main types. Business-to-consumer (B2C) platforms like Amazon and eBay sell primarily to end users. Although they reach a wide audience, they are not so relevant for natural ingredient suppliers whose main buyers are usually businesses and not consumers. For this sector, business-to-business (B2B) platforms are more interesting because they connect suppliers with other businesses, such as cosmetics manufacturers. In particular, they can give access to smaller buyers who want to place smaller orders. These buyers can be hard to reach through traditional sales channels. Examples of B2B platforms for the natural ingredients for cosmetics sector include:
- Connature. A platform specifically for sustainable industry professionals, buyers and distributors of raw materials and cosmetic ingredients. Connature connects exporters from low and middle-income countries (LMICs) with global cosmetics companies. They focus on environmentally responsible practices. This platform is particularly useful to promote your sustainability credentials and build relationships with buyers interested in ethical sourcing.
- 1-2-Taste. Specialises in serving small and medium-sized producers by offering raw materials and technical services like consulting and market intelligence. The platform helps exporters to enter international markets and gives access to tools that help with informed decision-making.
- Covalo. A platform for sourcing ingredients, packaging and services in the cosmetics industry. It makes it easier to find suppliers and partners, and offers exporters a way to connect with buyers and expand their market reach.
- SpecialChem. A digital marketplace for chemical ingredients, including those used in cosmetics. Its big database lets exporters promote their products and connect with potential buyers. This makes it a useful tool to reach niche markets.
- UL Prospector. An advanced search platform for raw materials used in cosmetics, food and pharmaceuticals. Exporters like it because it has detailed product information and is used around the world. It makes it easier to connect with manufacturers and buyers who are looking for specific ingredients.
Figure 3: Covalo’s online B2B platform for cosmetic ingredients
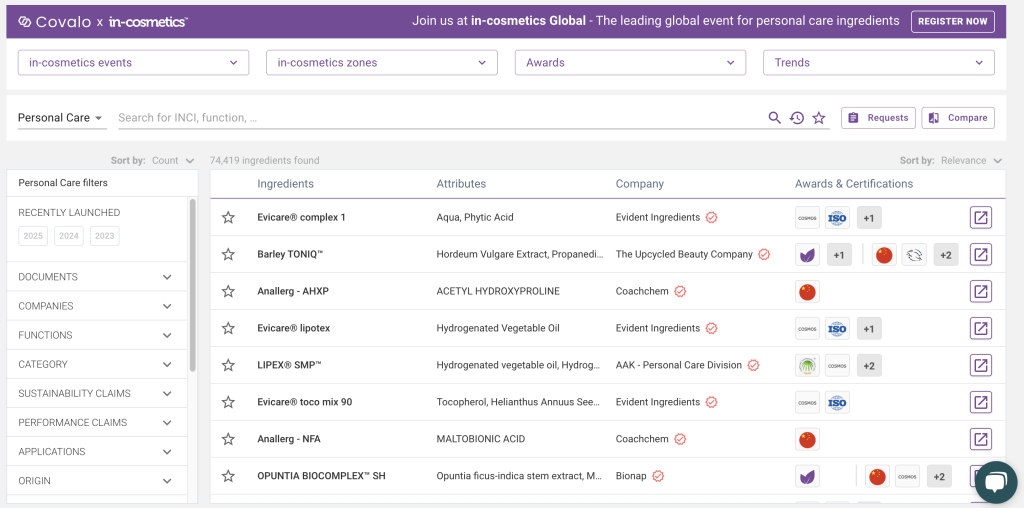
Source: Covalo Ingredients, 2025
Although it can be useful, e-commerce is not always the right solution for every supplier. For example, suppliers who already have customers may not need to switch to e-commerce. Other possible barriers include problems with the internet connection, poor transport networks and logistics and, sometimes, high risks and costs that outweigh the benefits. To use e-commerce platforms effectively, exporters need:
- A stable internet connection;
- Enough resources to maintain the platform, respond to customer queries, update product information and manage orders;
- A good knowledge of e-commerce and online sales management; and,
- A bank account that is able to receive online payments.
Tips:
- Check that the platform you are interested in already sells products that match your product range. That ensures that you connect with relevant buyers.
- Compare the costs and charging models of the marketplaces you are thinking about. Some charge a commission for each transaction, others a subscription or a flat fee. Platforms that offer more help in finding buyers may charge more for their services. Ask for a free trial to check that the platform is right for you and your product.
- Because online shoppers have a wide range of products to choose from, be aware that you may have a lot of competition. Just showing your product is not enough to make sure that you reach clients. You still need to promote your product and show that it is worth the money.
- Read What is a B2B marketplace? to better understand B2B e-commerce platforms and how to make the most of them.
7. Improve efficiency with business and inventory management tools
As an exporter of natural ingredients for cosmetics, acting professionally is essential to build trust with buyers and set up smooth business processes. Using business and inventory management tools will help you to streamline your operations, track inventory and improve your overall efficiency. They help you to manage your resources effectively, keep an eye on stock levels in real time and give buyers accurate information. This is all very important for success in competitive markets like Europe.
Business management software packages like ZOHO, HubSpot and Odoo make it easier to make administrative tasks easier and bring them together in one place. These solutions are ideal as they are easy to use, customisable and flexible. They also offer free basic plans and some work in mobile applications. ZOHO provides features like customer relationship management (CRM), invoicing, financial tracking and task management. HubSpot, widely recognised for its CRM capabilities, offers tools for sales, marketing and customer service so that exporters can build strong relationships with buyers. Odoo combines CRM, inventory, accounting and project management into a single platform. That is why it is a flexible choice for businesses of all sizes. By merging multiple functions into a single tool, these platforms reduce the need for manual processes, save time and minimise errors.
Video 3: Example of ZOHO inventory management for growing businesses
Source: ZOHO software, 2016
Apps that help you manage your stock are very important for exporters of natural ingredients for cosmetics. Tools like ZOHO Inventory and Fishbowl let you track stock levels, monitor product movements and predict demand. In particular, they make sure that sensitive raw materials are managed efficiently. That reduces waste and prevents overstocking. They also let you give accurate information about product availability and delivery times. This is very important to keep your customers happy.
Using business and inventory management software improves your professionalism as an exporter. Buyers really like working with suppliers who can give them correct and up-to-date information about their products. These tools let you communicate clearly, create professional invoices and deliver consistent service. If you can track inventory and manage operations digitally, you will also be seen a reliable partner in the natural cosmetics industry.
Tip:
- Check and compare the prices of the solutions you are interested in. Many software providers offer free plans for basic functions and charge extra for additional or more advanced features.
8. Unlock digital potential with AI-driven tools
Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing SMEs around the world by offering them powerful solutions for agriculture, supply chain management, quality control and market access. Nowadays, most of the solutions mentioned above use AI to help exporters in the natural ingredients sector improve efficiency, reduce costs and make traceability cheaper, easier and more customised.
You need a gradual approach to digitalisation. Follow the steps below to adopt and maintain digital tools smoothly and efficiently.
- Lay the foundations. Start by adopting mobile technology to improve your communications and market access. In farming, for instance, use apps to keep an eye on crop health, to process secure cross-border payments and to secure mobile-based microloans.
- Build a presence. Join B2B marketplaces to connect with European buyers. In this area, AI-powered chatbots like Zenvia and Tars automate customer interactions and so improve buyer engagement.
- Optimise the production and supply chains. AI and IoT (the internet of things) can help you improve quality control and efficiency thanks to tools that, for example, monitor pesticide levels, ensure regulatory compliance, track certifications and increase trust in the supply chain.
- Expand using AI and automation. AI-powered forecasting tools like Trendalytics and Spate help you as an exporter to spot market trends and, for example, to adapt your offering to meet formulator, laboratory and storytelling expectations.
- Keep improving. For long-term growth, apply AI-driven automation to your logistics, inventory and market intelligence activities. Because AI solutions are evolving rapidly, it is important to keep yourself updated and to keep your operations as efficient as possible.
- Stay informed about AI solutions throughout the supply chain. AI is revolutionising the formulation process, helping SMEs to access solutions that both improve transparency and reduce costs. Companies like The Good Face Project offer valuable insights into how algorithm-driven formulation tools can help brands and suppliers design compliant, sustainable and market-ready cosmetic products. That platform not only speeds up formulation but also ensures alignment with changing regulatory and consumer trends.
Video 4: Cosmetic formulation and regulatory platform: meet the Good Face Project
Source: The Good Face Project, 2023
9. Get support from national and regional organisations to go digital
Digitalisation can make you much more efficient and credible as an exporter of natural ingredients for cosmetics. But adopting digital tools takes time, investment and training. Many suppliers face challenges such as high adoption costs and a lot of learning to be done, which make outside support essential. National and regional organisations, and international projects, often offer useful assistance to help exporters make the digital transformation.
A number of organisations provide resources, training and financial assistance to exporters who want to go digital. Here are some which are relevant to the natural ingredients for cosmetics sector:
- Centre for the Promotion of Imports (CBI). Offers exporters practical studies, market trends and product-specific intelligence tailored to the natural ingredients sector. Its resources also include information on finding buyers and adopting socially responsible practices.
- Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO). Offers lots of publications and data on agriculture, focusing on sustainable practices and market developments. Exporters can find knowledge about production techniques and global trends.
- Committee Linking Entrepreneurship – Agriculture – Development (COLEAD). Offers lots of courses and resources for exporters, including self-study materials focusing on sustainable agriculture and digitalisation in value chains.
- Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ). Supports digital adoption in low and middle-income countries (LMICs) through different initiatives aimed at improving traceability, transparency and operational efficiency in agriculture.
Regional projects also play a crucial role in promoting digitalisation among smaller producers and exporters. Here are some interesting initiatives in low LMICs:
- Digital Transformation Center Kenya. This project, led by GIZ, encourages digital innovation and adoption across various sectors, including agriculture. It supports SMEs and exporters in applying digital tools to become more competitive.
- National Initiatives for Sustainable and Climate Smart Oil-Palm Smallholders (NI-SCOPS). This programme, led by Solidaridad, wants to promote sustainable and climate-resilient practices by small oil-palm farmers. NI-SCOPS helps companies to follow international sustainability standards, creating better opportunities for global market access. Digitalisation plays a very important role in the programme’s strategy.
Figure 4: Africa Goes Digital (non-profit corporation) map and list of members
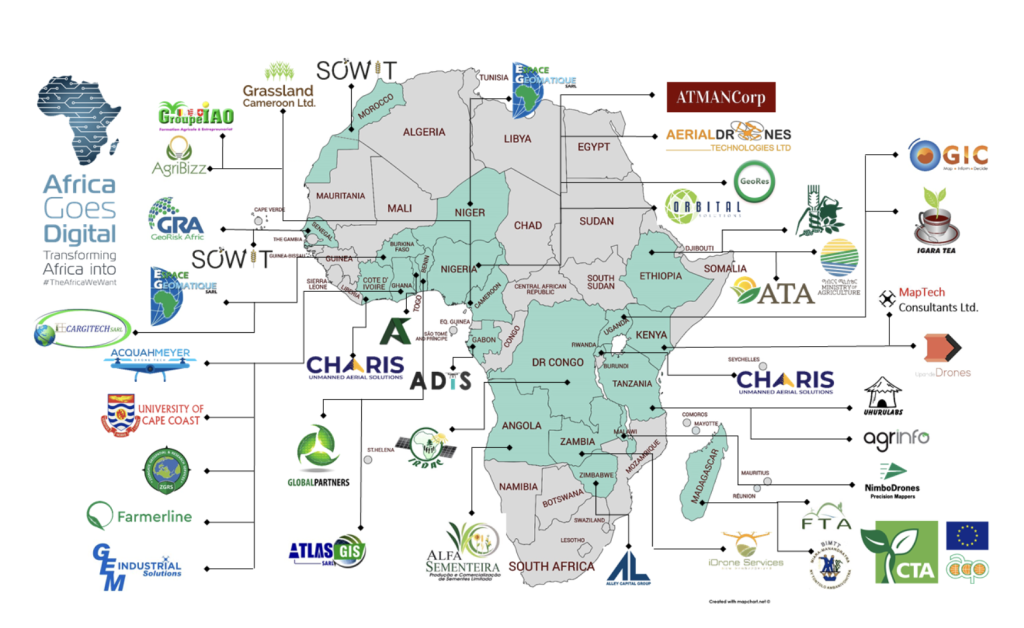
Source: Africa goes Digital
Tips:
- Find the sector association for your country or region and contact them to see if they can offer support.
- If you are an African supplier, check the Africa Goes Digital map and member list to find digital service providers in your country.
- Check out how the EU-LAC Digital Accelerator project is building bridges to speed up digital transformation in Europe, Latin America and the Caribbean, and see how it is connecting businesses and start-ups to boost digital transformation.
- Read the CBI studies Tips for doing business and Tips for organising your export, which provide practical tips to increase your chances of entering the European market.
ProFound – Advisers in Development carried out this study on behalf of CBI.
Please read our market information disclaimer.
Search
Enter search terms to find market research
