
Entering the European market for big data services
To enter the European market for big data services, you must comply with a variety of requirements. There is an increasing demand for corporate social responsibility standards and a greater emphasis on data protection and ethics. Competition is strong, but there are good opportunities if you can offer services that add value to the buyers’ companies at the right price.
Contents of this page
1. What requirements should big data services comply with to be allowed on the European market?
This section describes the most common requirements and certifications for big data services. It would be impossible to list all regulations, given the sheer volume of them and the fact that new legislation is always in the making. General market-entry requirements for software development are discussed in our study on Entering the European market for software development services.
What are mandatory requirements?
There is currently no specific EU legal framework to regulate big data services. Such services are nevertheless subject to a range of horizontal laws and principles, including on the protection of data and privacy and on the ethical use of data.
Protection of data and privacy
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is designed to protect the privacy of individuals in Europe from data breaches. Because it has been incorporated into the European Economic Area (EEA) Agreement, it is also enforced in Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway. France has its own France Data Protection Act.
Under the GDPR, any company or individual that processes personal data is responsible for protecting these data. Although not all big data projects entail personal data (e.g. names, email addresses, bank details, social media content, photos, IP addresses), many do. Given the expected increase in the personal-data aspect of big data development, compliance with the GDPR is highly relevant for you.
Within the next few years, around 75% of the world’s population is expected to be subject to regulations similar to the GDPR. This means that the protection of data and privacy will soon be necessary in the EU, as well as in most countries throughout the world.
Ethical use of data
Data are not the same as facts. Data can also be biased, and this can lead to ethical dilemmas that must be addressed.
Suppose you have developed an application to screen CVs and shortlist candidates for interviews. The application uses an algorithm that is based on historical data of successful employees in the company. As it turns out, however, in the past, the company’s hiring process was biased in favour of male candidates. This might have been due to any number of factors, including historical hiring practices, gender stereotypes and the presence of a predominantly male workforce.
If the algorithm is trained on this biased dataset, it is likely to learn and repeat the same bias. It might thus start favouring male candidates, even if their qualifications are similar to or less suitable than those of female candidates. As a result, the hiring process could become biased against women, even if the company intends to promote fair and equal opportunities.
Data privacy is one of the main ethical issues with big data. To prevent big data from being used for the wrong purposes, it is important to implement ethics within the code.
Artificial intelligence (AI) raises complex ethical issues. The following are the three greatest concerns:
- Privacy and surveillance
- Bias and discrimination
- Deception and manipulation
Given the rapid evolution of applications and uses of big data, it is important to keep up with developments. European buyers expect this from their providers, so that they can deliver ethical services.
Tips:
- If you are working with big data for artificial intelligence, it is important to stay up to date on the topic of ethics in AI. The council of Europe is a good source to start. See also the European Commission’s Ethical Guidelines for trustworthy AI. In addition, the European Commission is currently working to develop an Artificial Intelligence Act.
- Prioritise ethical considerations in your big data operations. This will allow you to build trust with your buyers. Prioritise data privacy, strive for objectivity, be transparent and accountable, and continuously assess and improve your ethical practices.
What additional requirements do buyers often have?
Most European buyers demand requirements relating to technical knowledge and experience, corporate social responsibility or project management.
Technical knowledge and experience
European buyers often require knowledge and experience in programming languages (e.g. Python, R, Java, Scala, TypeScript, Julia and C++), neural network architectures and natural language processing (NLP). Some require big data technologies (e.g. SPARK, Hadoop, Cassandra, MongoDb) or data mining tools (e.g. Rapid Miner, KNIME, Apache Mahout). Others require specific algorithms and frameworks (e.g. deep learning algorithms, PyTorch, Theano, TensorFlow, Caffe, Scikit-learn, NumPy).
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Most European buyers of big data services appreciate certification relating to corporate social responsibility (CSR). Some even require it. The following documents contains information on what it is, why it is important and how to obtain it it: Tips on how to go green in the outsourcing sector; Tips on how to become a socially responsible exporter in the outsourcing sector.
A Kenyan provider of big data services, Impact Sourcing, successfully integrates green and social practices and uses them as a unique selling point (USP). The website immediately demonstrates that the company has a clear vision and values concerning the social and green aspects of outsourcing. The services, customers and project examples are clear, and the landing page has multiple calls to action (CTAs), including a message box and subscription to the company’s newsletter.
Buyers require sustainability, including with regard to energy use. This can be achieved by:
- Working with energy-efficient software
- Offering big data services that contribute to energy savings for your buyers
Once you have decided to be mindful of the amount of energy your services consume and you have started to set and achieve goals for reducing your energy use, you can profile yourself as a conscious sourcing provider. This will give you a competitive advantage over other providers.
Agile project management
Many European companies have adopted ‘Agile’ project management. Although this form of management is losing popularity in some industries, it is currently the best project management tool for many big data services. Familiarity with — and certification in — Agile working methods might give you a competitive advantage.
Popular Agile certifications include: PMI-Agile Certified Practitioner, ICAgile Certified Professional, AgilePM Foundation, Certified ScrumMaster, Professional ScrumMaster and SAFe Product Owner/Product Manager.
What are the requirements for niche markets?
Each niche market has its own requirements. In this section, we provide several examples and explain how to find the requirements for the market you choose.
In healthcare, Health Level 7 (HL7) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) are important. In the automotive industry, MISRA and AUTOSAR are the two main coding standards used, but ISO 26262 and ISO 15504 are also applicable. For country-specific information, please consult governmental websites. For example, if you plan to export to Germany, consult the website of Bitkom, Germany’s digital association.
Tips:
- Learn from your clients and monitor potential clients to see which requirements they consider important. Perhaps you can work together on certifications or social goals.
- Identify which sector-specific standards or codes are available for your product (e.g. by asking your sector association or your buyer) and the extent to which your buyers would like for you to implement them.
- Read our study on general market entry requirements for the outsourcing sector.
2. Through what channels can you get big data services on the European market?
The European market for big data services can be segmented both horizontally and vertically. You can tap into these segments through several different market channels. The most preferred market channel for big data service providers is the search for strategic partners. Depending on the product or service you offer, online platforms could be another good market channel.
How is the end-market segmented?
The market can be segmented horizontally (application) and vertically (end-user industry). Experts agree that the market is not as fragmented as it was a few years ago, but it is also far from being consolidated. This means that many opportunities can still be found. This is especially because buyers of big data services used to mainly be large companies and governmental organisations, but the market is now also moving towards SMEs.
Figure 1: Horizontal and vertical market segments with opportunities for service providers
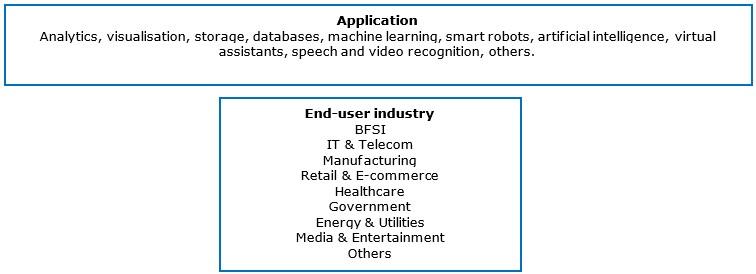
Source: Globally Cool
In 2022, the banking financial services and insurance (BFSI) segment dominated the market in Europe. This is because of the strong growth of the banking sector in the region, which will require big data services to process the large amount of data being generated and to organise and comprehend customer insights.
Source: Stellar Market Research
Buyers of one application might also be interested in other big data applications. For example, healthcare buyers might also be interested in pricing analytics and risk analytics. The same applies to manufacturing buyers, who might like to work with transportation analytics and workforce analytics.
Through which channels do big data services arrive on the end-market?
Most big data services arrive on the end market through strategic partners or online sales platforms. The situation is the same in most EU countries.
Figure 3: Trade structure for outsourcing big data services in the European market
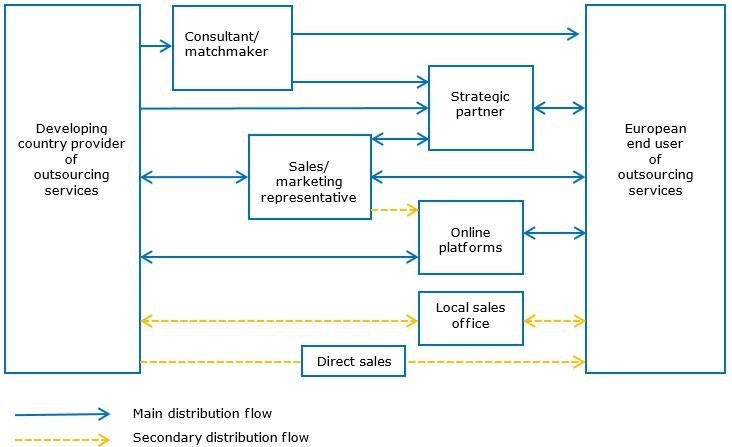
Source: Globally Cool
Strategic partner
There are several types of strategic partners. Examples include independent software vendors (ISVs), outsourcing service providers (OSP), outsourcing management agencies and consultancies. You can find a strategic partner either directly or by working through a consultant or matchmaker. Because many European companies prefer to deal with a local contact person, an intermediary is a good option. A European service provider that is similar to your company is likely to be the most suitable contractor.
The relationship between a strategic partner and a subcontracted supplier is characterised by the following:
- Trust
- Interdependence
- A structured relationship (functions, tasks, communication and procedures)
- Often limited marketing visibility and market access opportunities for the subcontracted supplier
- No intellectual property (IP) rights, or a loss of IP rights for the subcontracted supplier
- Work on an if/when necessary basis
Tips:
- Attend relevant industry events (online or in-person) in your target country to meet potential partners and competitors. This would also allow you to learn more about their business culture. Attend events relating to big data, like the Big Data Conference Europe in Lithuania, the Big Data Expo in the Netherlands or any of the top 14 big data conferences in 2023 (this list will be updated to 2024 soon). Do your homework, and select events very carefully. Attend only events that fit your profile well. Many directories of trade events are available online (e.g. 10Times and UK Exhibitions). Use big data industry associations or outsourcing associations to find potential customers in Europe. Examples include the Big Data Value Association and the Associazione Big Data (Italy).
- Use general IT industry associations to find potential customers. Examples include Bitkom and Eco in Germany, NLdigital in the Netherlands, and techUK and BIMA in the United Kingdom. If you specialise in a particular industry, you can also use associations for that niche (e.g. the Association of British HealthTech Industries).
Consultants/matchmakers
A consultant or matchmaker is a person or company with many relevant contacts in a specific market segment or industry. Intermediaries are door-openers, and not agents who make cold calls or send cold emails. Always properly inform your consultant/matchmaker about your company. They speak with many potential customers and often create long lists of potential outsourcing providers. The more information they have on your company and the better they understand your capabilities, the more they will be able to spread the word about you.
If you work with a consultant/matchmaker:
- The consultant/matchmaker will make appointments with prospects for you.
- The presentation and sales process will remain in your own hands.
- You will pay a retainer and a success fee (which can be expensive).
- The consultant/matchmaker will usually have multiple clients.
- You will need to set clear expectations and objectives to measure their performance.
The ‘retainer + success fee’ construction can be expensive. The success fee depends on what the intermediary has delivered, but you must pay the retainer (usually a fixed monthly payment) regardless of performance. Together, these fees should provide a strong motivation for the intermediary to deliver: the retainer should be high enough to cover some of the costs, but low enough to encourage delivery. A contract drafted by a lawyer, is a must.
Matchmakers make appointments with prospects for you, but the presentation and sales process remain in your own hands. This means that a consultant or matchmaker is a good option for you if you feel comfortable taking care of the presentation and sales process yourself.
It is important to include an exit strategy in the contract. This means that you should clearly define a brief period after which the contract can be terminated without any further consequences. This period is usually not longer than three or four months (after which the contract will be evaluated and can be terminated — e.g. for non-delivery — or extended for another period). For this period, the consultant or matchmaker should have clearly defined delivery expectations and targets (e.g. the number of relevant contacts, meetings and leads). You could also negotiate a trial period.
Tips:
- Work with a good lawyer who knows the laws of the country in which the intermediary resides and who has previous experience with this type of contracting. Pay special attention to exit clauses, success criteria, deliverables and payments.
- Consider who might be a good sales representative for your company. Although convenient, your uncle who lives in Germany might not be the best choice.
- Before the COVID-19 pandemic, various organisations arranged matchmaking sessions or missions in which companies from developing countries could participate. Find out whether any organisations in your country currently offer matchmaking sessions (either online or offline).
Sales/marketing representative
Another type of intermediary is a sales/marketing representative. These representatives are more involved in the sales process than consultants/matchmakers are.
When working with a sales/marketing representative:
- The sales/marketing representative will contact prospects for you.
- The sales/marketing representative will also make the sales and, in some cases, manage projects.
- You will pay either a retainer and a success fee (which can be expensive) or a fixed monthly fee.
- The sales/marketing representative can either have multiple clients or work exclusively for you.
Good sales/marketing representatives have large, relevant networks. For this reason, they will not make cold calls to bring in services for you. Their success fee is often a percentage of the projects they bring in. Paying a sales/marketing representative will increase your expenses, but it will also free you to focus on your core business and to search for other markets by yourself.
Online platforms
Electronic marketplaces are an inexpensive marketing tool that can make direct sales easier. Although they mainly contain smaller projects for freelancers, they could lead to pilot projects for your company. For this to happen, however, you must have excellent end-market knowledge.
Online platforms also offer the opportunity for companies to expand their capacity and assemble virtual teams if needed.
Tip:
- You can also find leads and display your knowledge on LinkedIn and Github Marketplace. Freelancers and very small companies can find leads on UpWork, Fiverr and Freelancer. For more information on finding business through online.
What is the most interesting channel for you?
Working with a strategic partner is the most realistic market entry channel. In such arrangements, European service providers subcontract big data service assignments that end-user companies have contracted to them. Which channel is right for you depends on your type of company, the nature of your service, your target market and the resources available for market entry. Be aware that, regardless of the channel you choose, your own marketing and promotion will be a vital part of your market-entry strategy, for which you will be responsible.
Tips:
- Create an ‘ideal’ client to help you customise your offer: for example, ‘a big data service provider with fewer than 200 staff members in the Rhineland area, specialised in forecast and modelling for the transport sector’.
- Have a professional, high-quality company website, where you present full, accurate and up-to-date details of the products/services you offer. Make it compatible with smartphones, tablets and other mobile devices. In addition, invest in search engine marketing (SEM) and search engine optimisation (SEO), so that potential customers can easily find you online. A good LinkedIn profile is also important.
3. What competition do you face on the European big data services market?
Which countries are you competing with?
India, Malaysia and Egypt are likely to be your strongest competition from countries outside of Europe. Poland, Hungary and the Baltic countries are your strongest European competitors.
The Global Services Location Index (GSLI) ranks the competitiveness of ITO/BPO destinations based on four categories: financial attractiveness, people skills and availability, business environment and digital resonance.
Table 1: Global Services Location Index
|
Financial attractiveness (35%) |
People skills and availability (25%) |
Business environment (25%) |
Digital resonance (15%) |
|
Compensation costs |
ITO/BPO experience and skills |
Country environment |
Digital skills |
|
Infrastructure costs |
Labour force availability |
Country infrastructure |
Legal and cybersecurity |
|
Tax and regulatory costs |
Educational skills |
Cultural adaptability |
Corporate activity |
|
|
Language skills |
Security of IP |
Outputs |
Source: Kearney analysis
Source: Kearney 2023
The countries mentioned in Figure 4 are generally the strongest competitors as outsourcing destinations. For SMEs from emerging economies that provide big data services, however, other countries are more likely to be direct competitors (see Figures 5 and 6).
Competition from non-European countries
Source: Kearney 2023
India: Once again, the Number 1 destination
India continues to lead the Global Services Location Index (GLSI). This position is due primarily to the country’s unique combination of low-cost services, large talent pool and English-language skills. This attractive profile makes India a particularly strong competitor on the outsourcing market.
India is also investing in talent regeneration. This is necessary, given that India is mainly known as a cheap bulk destination.
Because big data services are increasingly demanding innovative thinking and highly skilled work, India will need to step up its game if it wishes to stay in the lead — and it is doing just that. The Indian government has launched programmes aimed at upskilling 4.7 million people on i4.0 technologies (based on big data), including AI, 3D printing, drones and the Internet of Things (IoT). The country is also strengthening its science, technology, engineering and math (STEM) backbone and educating young students in crypto, AI and other technologies. The new National Data Governance Policy will reinforce India’s status as a high-skill, low-to-medium-cost market and fulfil its vision to ‘Make AI in India’.
Convergytics
Convergytics is a big data analytics company that was founded in India. The company specialises in growth analytics with a focus on retail and CPG. The company provides services that help companies to enhance customer satisfaction, increase ROI for marketing and engage in innovation to stay competitive.
Malaysia: A good, well-educated English-speaking workforce
Malaysia ranks third in the GLSI, primarily due to its large and relatively highly educated workforce, which possesses favourable English-language skills. Malaysia has a strong tech industry with a good reputation as a destination for ITO and BPO. The country nevertheless needs to invest heavily in educating new talent and retaining its current talent. In addition, their advantage in terms of labour costs is decreasing.
The country focuses on developing digital expertise and embracing new technologies. The Malaysian government actively provides support to help tech startups to expand throughout the country and the surrounding region. Malaysia’s workforce is known for its expertise in areas like cloud computing, analytics, AI and software development. Each year, these skills add around EUR 105 billion to the country's GDP.
The government has also launched the Malaysia 5.0 initiative, which includes such efforts as the #MyDigitalMaker Movement, eUsahawan, Premier Digital Tech Institute and the Digital Skills Training Directory. The initiative is intended to enhance and update the skills of the population.
Egypt: Regional offshore champion that needs to work on its digital focus
From 2021 to 2023, Egypt dropped eight places in the GSLI ranking (from 15 to 23). This was mainly due to its lack of digital focus. Another major factor had to do with the rising cost of labour, combined with the volatility of the country’s currency.
Despite these setbacks, Egypt is now starting to focus on developing new technological skills. Public–private partnerships have been established through the Information Technology Industry Development Agency. The agency’s goal is to improve the access of young IT professionals to the labour market and to enhance their employability, whilst fostering their professional growth. This will help Egypt to maintain its position as a regional talent pool and offshore hub.
In addition to the challenges described above, European buyers often have security concerns when deciding whether to outsource to Egypt. Although Egypt has made strides in improving its cybersecurity and data-protection measures, it is still important to consider security concerns, including those relating to cyberthreats and political instability.
The same applies to infrastructure reliability. Although the Egyptian IT infrastructure has improved, there may still be occasional issues with internet connectivity and the reliability of the power supply.
Competition from European countries
European countries pose significant competition as well, and particularly Poland, Hungary and the Baltic countries.
Source: Kearney 2023
Poland: Tech savvy combined with competitive labour costs
Poland is currently ranked 13th in the GSLI, one place higher than in 2021. The country is especially interesting as a destination for outsourcing big data services, as it has made major investments in technology driven by big data.
The Polish IT outsourcing ecosystem combines around 700 business service centres located in Warsaw, Kraków, Łódź and Wrocław. Poland is home to the world’s third most-skilled population of programmers. In addition to having experience working with technologies based on big data, Polish software engineers are good in mainstream programming languages.
Alongside this skilled workforce, Poland has competitive labour costs, a high level of proficiency with English, a stable political and economic environment, and a good IT infrastructure.
Poland’s cultural proximity and similar time zone make it an interesting location for potential European buyers of big data services.
Effective Soft
Effective Soft is a software development company that was originally established in Poland, and it now has an office in the USA as well. The company has extensive experience in handling big data. As mentioned on Effective Soft’s ‘about us page’, the company has its own research and development programme. It also adopts an open approach to quality and professionalism at each level — a feature that is highly appreciated by its partners.
Hungary: A popular outsourcing destination that keeps investing in IT
Hungary is a leading provider of highly skilled IT personnel, making it a prime option for nearshore outsourcing in Europe. Between 2019 and 2021, the country jumped six spots in the GSLI ranking, and it advanced an additional 18 places from 2021 to 2023.
Hungary’s heavy investments in emerging technologies (e.g. IoT) and its favourable policies (e.g. financial support) for AI and IT have led companies to establish R&D centres there.
Hungary offers many of the same advantages as Poland for outsourcing big data services, including a skilled workforce, cost-effectiveness, a strong IT infrastructure, data-security compliance and a supportive business environment. The choice between Poland and Hungary often comes down to specific project requirements, existing partnerships and other factors (e.g. the availability of specialised skills or cost differentials between the two countries).
It is important to note that the labour costs for big data professionals are increasing rapidly in both Poland and Hungary. These countries are therefore interesting to target for strategic partnerships.
Baltic countries: Emerging outsourcing destinations that invest in big data technology
The Baltic countries (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania) have gained recognition as emerging destinations for outsourcing, including for big data services. Although they do not hold the highest rankings in the GSLI, they are stable forces and attractive outsourcing destinations for European companies.
The Baltic countries are known for their skilled IT workforce and strong IT infrastructure, as well as their cost-effective solutions, innovation hubs and government support. They are a preferred choice for many EU buyers due to their cultural proximity, EU membership and stable political environment.
In addition to their advantages, the Baltic countries are also subject to a number of limitations, including a smaller talent pool, high competition for talent and relatively high prices compared to some other outsourcing destinations (e.g. Egypt).
Tips:
- Use the services of your national export promotion agency and actively participate in the creation of export strategies.
- Compete on skills, and not on price.
Which companies are you competing with?
The following are several examples of big data service providers:
Marketeers
Marketeers is an Egyptian data and analytics company specialising in market research and providing comprehensive insight and data-driven solutions to businesses seeking a competitive edge. The company has a dedicated team of industry experts and offers customised research services to help companies make informed strategic decisions. Marketeers Research is known for its in-depth market analysis and actionable recommendations that drive business growth and success.
Hiflylabs
Hiflylabs is a big data company based in Hungary. The company excels in providing advanced data solutions and AI-driven applications. It specialises in harnessing the power of machine learning and AI to solve complex business challenges. With a focus on cutting-edge technology and data-driven strategies, Hiflylabs empowers organisations to optimise operations and make data-informed decisions for sustainable growth.
BigData Ghana
BigData Ghana is a big data company that provides business solutions based on big data for many different industries. The company has won the Digital Earth Africa Innovation Challenge. Its excellent website clearly states the services offered, along with client testimonials and companies and projects the company is working on.
Tips:
- As illustrated by the companies mentioned above, it is important to emphasise the skills of your workforce and the solutions offered by your big data services. You should also avoid being a bulk destination and display your best work (portfolio) on your website. This type of specialisation creates opportunities.
- Search company databases to find more competing companies. Some of these databases are free of charge (e.g. company.info). Others are made available through chambers of commerce (e.g. Kamer van Koophandel in the Netherlands) or commercial providers (e.g. BoldData). Identify which databases are suited to your search, and use them to create a list of potential customers to target.
Which products are you competing with?
In the big data services industry, the product is the service. The real question is thus, ‘What makes one service provider different from another?’ The answer comprises a variety of characteristics, including technical knowledge, available capacity, analytical skills, understanding of various algorithms, references, flexibility, scalability, reliability, communication and language capabilities, quality management, security infrastructure, vertical and/or horizontal market focus and niche-market orientation. The location (country) of the service provider is also an important factor.
Unless you are selling your own big data products directly to the European market, your products consist of the services you provide.
If you are selling big data-based apps, you should be aware that they are accompanied by other IT-related tasks. They require software updates, routine maintenance and continuous strategy for the development and implementation of new features. If you can offer to perform these tasks continuously, so that the users of your product can focus on their core business, it will make you stand out from your competition.
There is space in the market for innovation and developing original products based on big data. The market is very challenging, however, especially for providers from developing countries.
There might be possibilities for developing and selling applications with capabilities relating to big data (e.g. AI, ML, IIot/IoT) for specific sectors. Market knowledge and niche-market focus are essential in this regard. There are nevertheless many examples of successful big data start-ups, including those on the following lists: AI start-ups in Indonesia and Egypt, and ML start-ups in Uganda.
Tips:
- Research the end-user industry that you would like to target. Subscribe to mailing lists from organisations that combine that end-user industry with technological solutions (e.g. the Association of British HealthTech Industries).
- You can develop your own big data services, even combined with your own applications. Alternatively, you could offer to work with systems your buyer already has in place, for example, if you have built up significant experience in Amazon Web Services (AWS). Find out how to gain a competitive advantage based on factors including quality, cost, technology or product characteristics. If your service is a relative commodity, you should focus on a niche market — especially if you can find one that is underserved or has the room/need for digital transformation. For ideas, read blogs or articles that mention big data skills.
4. What are the prices for big data services?
Price is one of the main reasons for European companies to outsource their big data projects to companies in other countries. Salaries make up a large share of costs in big data services. The average annual salary of a big data engineer in Western Europe is just under EUR 100,000. In offshore destinations, the salaries are usually significantly lower. Outsourcing to countries where wages are lower can thus lead to considerable cost savings.
It is important to note that the outsourcing of big data services usually involves big data jobs that are generally simpler than the tasks performed by big data engineers. For this reason, the price difference is not as large as it might seem from the previous paragraph.
The price for big data services is influenced by technological requirements, skill levels, project complexity, contract length and other requirements written in the Service Level Agreement (SLA). Your offer should include the price, along with your hourly rates and an honest estimation of the number of hours you expect to work on the project.
The prices for big data services are expected to remain high. The current skills shortages in Europe are expected to remain the same, or even increase within the next 5–10 years. Technological inventions will probably lead to a certain degree of automation in existing big data services. As a result, if you do not keep up with technological developments, the prices for your current services could be expected to remain stable or decline. If you manage to stay on top of the newest developments, however, you can make good money as a big data service provider, both now and in the foreseeable future.
You must also choose a price model for your product or service. There are three popular working models: the Fixed-Price Contract model, the Time and Material approach and the Dedicated Team model. The most common price model for software development services is the Fixed-Price Contract. This is an all-inclusive offer, where clients are billed according to pre-defined milestones (as listed in the SLA).
It is impossible to make an exact price breakdown. One reason is that big data projects are so diverse that there is no single price breakdown that will suit all (or even most) projects. A second reason has to do with the large amount of estimation required and the presence of unforeseen elements that make the process itself an estimation. The fact that big data projects change frequently raises other issues, including scope definition, change management and acceptance. One thing that is clear, however, is that European buyers are often less price-sensitive within niche or non-commodity markets.
European buyers often associate extremely low rates with poorer project quality. They are likely to assume that cheap service providers must have compromised on the skills and experience of their service developers, or even on their working conditions.
Tips:
- Study average prices in reports such as those published by Cleveroad, IT Jobs Watch or Iris Pricing Solutions. You should also research the average salaries for various roles in your work process through platforms like Payscale. Analyse your costs and profit expectations to calculate and decide on the right price for your service.
- Choose a type of pricing model for your outsourcing contract. For inspiration, view InventorSoft’s Top 10 Pricing Models to Consider in 2023). Go beyond setting the right price and work out your pricing strategy. This should include the preferred pricing model, payment terms and expectations, and how and when you will offer discounts.
Globally Cool B.V. carried out this study in partnership with Laszlo Klucs on behalf of CBI.
Please review our market information disclaimer.
Search
Enter search terms to find market research
