
Entering the European market for mobile application development services
You need to comply with a range of laws and regulations to enter the European market for mobile app development services, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Buyers have additional requirements that you will need to meet. Your main competitors are mobile app development companies from nearshore locations, such as Poland and Ukraine, and offshore locations, like India and the Philippines. The most effective way to enter the European market is by working with strategic partners.
Contents of this page
- What requirements and certifications must mobile application development services meet to be allowed on the European market?
- Through which channels can you get mobile application development services on the European market?
- What competition do you face on the European mobile application development services market?
- What are the prices of mobile application development services on the European market?
1. What requirements and certifications must mobile application development services meet to be allowed on the European market?
To enter the European market for mobile application (mobile app) development services, you need to comply with mandatory requirements and additional buyer requirements. Niche markets may also have specific requirements.
Market entry requirements for IT and business process outsourcing (ITO and BPO) are listed in our study on the requirements outsourcing providers need to meet. This chapter addresses the most common requirements for mobile app development services. New legislation is always being developed, particularly in relation to the European Green Deal (Europe’s roadmap to become climate-neutral by 2050) and the European Union’s (EU) digital transformation strategy. Make sure you stay up to date.
What are mandatory requirements?
The following legal requirements may apply to mobile application development companies that operate in the European market:
- Directive on the legal protection of computer programs (2009/24/EC);
- General Data Protection Regulation (EU 2016/679);
- Data Act (EU 2023/2854) and Data Governance Act (EU 2022/868);
- ePrivacy Directive (2002/58/EC);
- General Product Safety Regulation (GPSR – EU 2023/988);
- Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act – EU 2024/1689);
- European Accessibility Act (EAA – EU 2019/882);
- Cyber Resilience Act (EU 2024/2847).
The type of legislation that applies may vary depending on the company’s business model, target sector, and client.
Tip:
- Make sure you fully understand how each legal requirement affects the development process when creating mobile apps for European clients. For example, read Scanbot SDK’s article on how to ensure your mobile app complies with the EAA 2025.
What additional requirements and certifications do buyers often have?
European buyers often have additional requirements when choosing a mobile app developer. These include:
- Quality management systems, often ISO 9001 or CMMI;
- Information security management systems, preferably ISO 27001 compliant/certified;
- ISO-compliant software development, such as ISO/IEC/IEEE 12207;
- Ergonomics of human-system interaction, ISO 9241-210;
- Software testing, ISO/IEC/IEEE 29119;
- Agile project management methodologies.
Tip:
- Find out which certifications are relevant for you based on the market and customer needs and requirements. When considering a particular certification or standard, ask yourself three questions before you implement it. Is it good for my company? Is it good for my clients? Does it have marketing value?
Industry best practices
There are a few specific best practices for the mobile app development industry, such as:
- Apple's Human Interface Guidelines (HIG): These guidelines are a set of design principles, recommendations, and best practices that Apple provides to help developers create intuitive, user-friendly, and visually appealing iOS apps. They are crucial for iOS app development. They cover everything from user interface (UI) elements and navigation to system interactions and accessibility.
- Google's Material Design: This design system gives in-depth user experience (UX) guidance and UI component implementations for Android, Flutter and the Web.
- OWASP Mobile Application Security (MAS): This project offers an industry standard for mobile app security (OWASP MASVS), a list of common security and privacy weaknesses for mobile apps (OWASP MASWE), and a detailed guide for mobile app security testing and reverse engineering (OWASP MASTG).
Technical requirements and technologies
Mobile app development involves a range of technologies and programming languages. These depend on the specific platform and app requirements. The technologies you need to use depend on factors such as:
- The target platform (iOS, Android, or both);
- The app's complexity and performance requirements;
- The developer's experience and preferences;
- The project budget and timeline.
Figure 1: Factors to consider when deciding on the required set of technologies and programming languages
Source: Globally Cool
Native app development requires the following programming languages:
- iOS: Swift is Apple's programming language for developing iOS, iPadOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS apps. Swift is the preferred programming language, but some older iOS apps still use Objective-C;
- Android: Kotlin is a programming language for Android development. It is used by over 60% of professional Android developers. It is interoperable with Java. Java used to be the dominant language for Android development. Now, it is mainly used in older projects.
For cross-platform app development, the following technologies and programming languages can be used:
- React Native: Developers can use React Native to build apps for both iOS and Android using JavaScript;
- Flutter: Flutter is an open-source framework for building apps. It uses the Dart programming language to create cross-platform apps with a single codebase;
- .NET Multi-platform App UI (NET MAUI): This framework is used to build native mobile and desktop apps. It uses C# and XAML. You can use the platform to develop apps that run on Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows from a single shared codebase.
- Web technologies like JavaScript, HTML, and CSS can be used to build hybrid apps. They are often combined with frameworks like Ionic or Apache Cordova.
Other technologies and frameworks are also used in mobile app development. These include:
- Frameworks: Frameworks provide pre-written code and tools to streamline and speed up software development. Examples include SwiftUI (iOS) and Android SDK.
- Application programming interfaces (APIs) enable software apps to communicate with each other. APIs are used in many internet-connected apps. For example, social media apps use APIs so you can see and share posts from your phone.
- Databases: Mobile apps use databases to store and manage data. Examples include SQLite, Realm, and Firebase.
- Cloud services: Cloud platforms offer services for storage, authentication, and backend functionality. Examples inlcude Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure.
Low-code and no-code platforms for mobile app development are becoming more popular. These platforms require minimal to no coding to build an app; they have drag-and-drop visual modelers and point-and-click interface creation tools to develop apps. Examples include:
- No-code platforms like AppSheet, FlutterFlow, Adalo, and Thunkable;
- Low-code platforms like OutSystems and Mendix.
Soft skills
Besides technical knowledge and experience, developers must also have good soft skills. Clear communication helps them understand what clients need and work well together. This also builds trust. Skills like problem-solving and flexibility help developers tackle tricky issues and adapt to changes. Understanding what end-users want and making software easy to use is also important. Good leadership and teamwork keep everyone on track and motivated, making sure projects run smoothly.
Sustainability
Companies are often required to demonstrate their socially and environmentally sustainable business practices. Voluntary standards can help you demonstrate responsibility, such as ISO 26000 (social) and ISO 14001 (environmental).
Tip:
- Read about sustainability in ITO/BPO in our studies 7 tips on how to go green in the outsourcing sector and 7 tips on how to become more socially responsible in the outsourcing sector.
What are the requirements for niche markets?
Requirements for mobile app development can vary per industry and country. When planning to offer mobile development services in a specific niche, check the applicable requirements.
Country
For country-specific information, check the government websites. If you plan to export to Germany, check the Bitkom website, Germany’s digital association. In Germany, for example, the Federal Data Protection Act (Bundesdatenschutzgesetz – BDSG) supplements EU’s GDPR.
Industry
Different industries have different requirements. If you develop mobile apps for a specific industry, you need to take these requirements into account. For example:
- The Health Level 7 (HL7) is important in the healthcare sector;
- For finance, banking apps should comply with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA, EU 2022/2554), the Payment Services Directive (PSD2) and the PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for payment security.
Tips:
- Learn from your clients and check what potential clients require. You may be able to work on certifications or social goals together.
- Read Appinventiv’s guide How to Develop a PCI-Compliant Fintech App? if you develop finance apps.
2. Through which channels can you get mobile application development services on the European market?
The European market for mobile app development can be divided into several segments, such as by application, end user industry, platform, technology, and app category. The most promising channel to enter the European market is by working with a strategic partner.
How is the end-market segmented?
There are multiple ways to segment the mobile app development market:
- Horizontal segments: In this case you segment the market by application. Examples include utility apps (such as calculators, calendars, file managers, and cloud storage), and mobile payments;
- Vertical segments: This means segmenting the market by end-user industry. For example, travel and mobility, fintech and banking, and education;
- Platform: You can develop apps for different platforms, like iOS and/or Android;
- App category: You can focus on consumers, enterprises, and/or utilities;
- Technology: You can use different technologies to build apps, such as native, cross-platform, web, and/or hybrid;
- Monetisation model: There are a range of models, such as, free with ads, freemium / in-app purchase, subscription, paid apps, and/or enterprise licensing / SaaS (Software as a Service).
The mobile app development market in Europe is saturated. Apps are considered a commodity. However, new technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and (industrial) internet of things (IoT/IIoT), create new opportunities. There are still a lot of niche segments, so there is plenty of space for new ideas and innovation.
Figure 2: Market segments with opportunities for mobile app development companies
Source: Globally Cool
One potential opportunity is to focus on a niche market. Take the healthcare sector as an example. In the healthcare sector, you can develop apps for different types of clients and target groups, including patients, medical professionals and healthcare providers. Mobile apps also have many uses in the healthcare sector. You can create diet and nutrition apps, health monitoring apps, appointment scheduling apps, apps integrated with medical devices, electronic health record (EHR) apps and so on.
One company that specifically targets the healthcare sector is the Czech company Pears Health Cyber Europe. This digital marketing and communication company is active in the medicine and pharmaceutical industry. They specialise in mobile apps and video production for doctors and patients. Their mobile apps are used in more than 10 European countries.
Another example of an industry with a strong need for mobile apps is the fintech and banking sector. Mobile app development companies create mobile banking apps, digital wallet apps, money transfer systems, closed-loop wallets, currency exchange apps, investment and stock trading apps, and more. Examples of companies active in fintech app development services include Artkai (Poland), Orangesoft (Poland and USA), and Netguru (Poland). As a small service provider you should focus on specialised niche segments within this sector.
Tips:
- Focus on a niche market and specialise to avoid strong competition. This will also help to market yourself better. Then, focus on finding strategic partners in that niche.
- Research the end-user industry that you want to target. Find out what their needs are. Also research your competitors in the niche segment of your target market. Identify gaps in your target market and use that information to set yourself apart from the competition.
Through which channels do mobile application development services end up on the end-market?
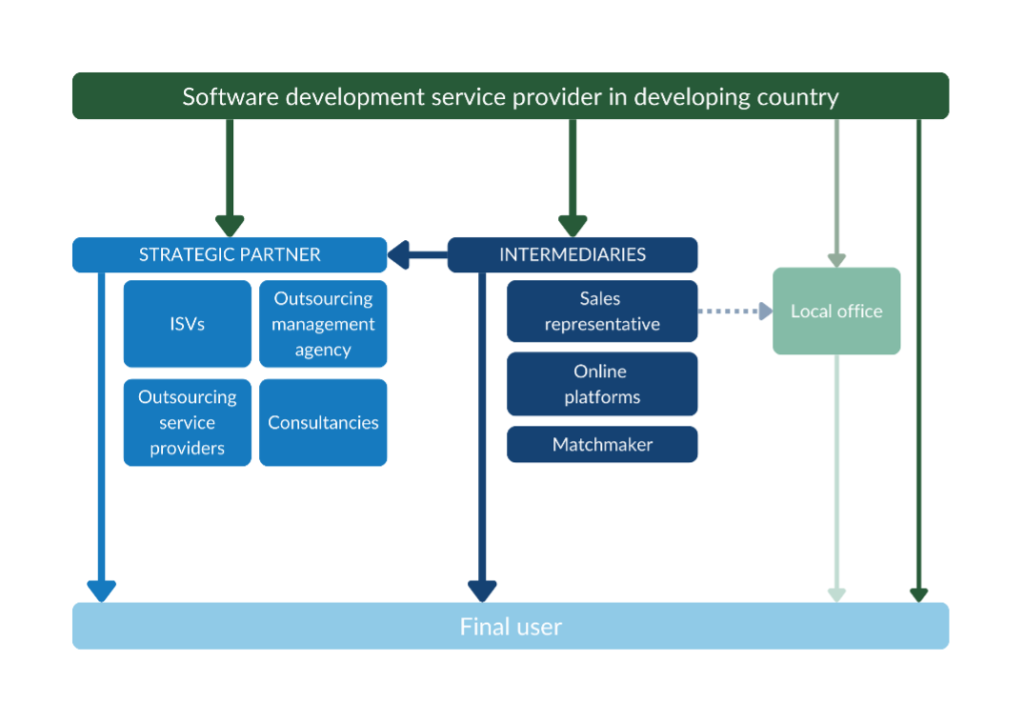
Figure 3 provides an overview of the trade channels you can use to enter the European market. This structure is very similar in every country. Working with a strategic partner is your most realistic option.
Figure 3: Trade structure for mobile app development services in the European market
Source: Globally Cool
Strategic partners
Working with a strategic partner is your most promising market entry channel. This could be Independent Software Vendors (ISVs), outsourcing management agencies, outsourcing service providers or consultancies.
A provider that is similar to your company (for example in terms of size, technology portfolio, and customer portfolio) would be most suitable. Ideally, this company should design, develop, market, and sell mobile app development services. For example, if your company targets niche segments in the healthcare sector, you should focus on finding European companies that develop mobile applications for these specific healthcare industry niches.
The relationship between a strategic partner and a subcontracted supplier (you) is generally characterised by:
- Trust;
- Interdependence;
- A structured relationship (functions, tasks, communication, and procedures);
- Potentially limited marketing visibility and market access opportunities for the subcontracted supplier;
- No intellectual property (IP) rights, or a loss of IP rights for the subcontracted supplier.
Please note that when you work with a strategic partner, they are the ones who will communicate with the end user about the mobile app you are developing. As a subcontractor, you will probably not appear in their marketing communications. You will be referred to as 'delivery centre'.
You can find a strategic partner either directly or by working with an intermediary. Because many European companies prefer to deal with a local contact person, an intermediary is a good option.
Tips:
- Attend relevant (online) industry events like WeAreDevelopers World Congress (Germany), Appdevcon (the Netherlands), or Mobile World Congress Barcelona (Spain) to meet potential partners and competitors. Research these events and select one that fits your profile. Make a list of relevant events using directories like 10Times.
- Use industry associations or outsourcing associations to find potential customers in Europe. For example, see the members of The App Association and the member list of Dutch Digital Agencies.
- Use general IT industry associations to find potential customers, such as Bitkom in Germany, NLdigital in the Netherlands, and techUK and BIMA in the United Kingdom (UK).
Intermediaries
You can work with an intermediary to find a buyer or strategic partner.
Matchmakers
A matchmaker is a person or company with many relevant contacts in a specific market segment. They do not make cold calls. Always properly inform your matchmaker about your company, so they can match you with suitable leads from their network.
If you work with a matchmaker:
- The matchmaker makes appointments with prospects for you;
- The presentation and sales process remains your responsibility;
- You often pay a retainer plus success fee (which can be expensive);
- The matchmaker often has multiple clients;
- You need to set clear expectations and objectives (and exit criteria) to measure their performance.
A retainer plus success fee can be expensive. The success fee depends on what the matchmaker has delivered, but you must pay the retainer (usually a fixed monthly payment) regardless of their performance. The retainer should be high enough to cover some of the costs, but low enough to encourage delivery. A lawyer must draft the contract.
You also need to include a trial period (usually ≤3-4 months) after which the contract can be terminated without further consequences. The delivery expectations and targets for this initial period must be clearly defined, such as the number of relevant contacts, meetings, and leads. Your contract should also have clear exit options.
Sales representatives
Another type of intermediary is a sales representative. These are more involved in the sales process than matchmakers.
If you work with a sales representative:
- The sales representative contacts prospects for you;
- The sales representative also makes the sales and sometimes manages projects to a certain degree;
- You often pay a retainer and success fee (which can be expensive), or a fixed monthly fee;
- The sales representative can have multiple clients or work exclusively for you.
A good sales representative has a large, relevant network, so they do not make cold calls. Their success fee is often a percentage of the value of the projects they bring in.
Online platforms
Electronic marketplaces are a cheap marketing tool that may make finding partners easier. There are several platforms that primarily cater to freelancers (individuals). However, there are also dedicated business-to-business (B2B) marketplaces.
Tips:
- Make sure that any selected matchmaker or sales representative has a large relevant business network.
- Be cautious if intermediaries only ask a success fee. This means that either they are excellent at their job, or they are desperate and may not (be able to) deliver. You should also be cautious if intermediaries want to work for you part-time besides their regular job. Often they are too busy to deliver.
- Work with a good lawyer who knows the laws of the country where the intermediary resides. They should also have experience with this type of contracting. Pay special attention to exit clauses, success criteria, deliverables, and payments.
- Look for leads on online platforms like UpWork, Freelancer, Fiverr, ITeXchange, Clutch, and pliXos. For more information on online marketplaces, please read our study about finding buyers on the European outsourcing market.
Local office
Another option is to set up a local office in your European target market. You can also open an office in one of Europe’s nearshoring destinations (for example Central and Eastern European markets), which is generally cheaper.
Having a local presence makes it easier to build long-term relationships with customers through personal contact. It also increases your credibility, builds trust, and allows you to retain complete control over your marketing and sales activities. However, this can be difficult, as it requires a lot of experience and large investments. Many IT service providers in developing countries are simply too small. They do not have the financial strength or enough verified market opportunities for this.
Tips:
- Be aware that establishing a local sales office is very costly and you need a strong financial position.
- Consider establishing your own office if you already have a client base in the target market, or if you have a well-founded indication of the demand for your services/products. If you decide to establish an office, involve your sales/marketing representative.
- Look for alternatives to lower your costs, such as business incubators or government incentives to bring your business to a particular country/region.
Direct sales
You can also try to sell your mobile app development services directly to European end-user companies. Many European companies are looking for cost reduction and delivery capacity, which developing countries can often provide. This is one of your unique selling points (or at least a competitive selling point). However, you should be aware that these end-users might not have qualified IT staff to work with.
Direct sales require experience in the European market and are most suitable for relatively large providers that want to target large European end-users. Your best bet is to focus on a small, underserved niche market. For most suppliers from developing countries, however, it is very challenging to sell mobile app development services directly. Having existing customers in Europe will help, because you need references for direct sales.
Tips:
- Combine offline and online promotion channels to develop as many contacts as possible. This maximises your chances of finding suitable partners/customers. Use social media platforms as a marketing tool. LinkedIn can be particularly useful for making initial contacts and conducting market research.
- Build a professional, high-quality company website, where you present full, accurate, and up-to-date details of your product/service offering. Make it compatible with mobile devices and invest in Search Engine Marketing and Optimisation, so potential customers can easily find you online.
App stores
If you create your own mobile app, you can sell it through an app store (such as Google Play and App Store). An app store is a marketplace where users can browse and download apps.
The app store may take some time to approve your app. They need to check the privacy, security and safety of each app. Reaching the right users can also be a challenge. You will need to spend a lot of time and effort to target the right users. You should also be aware that the mobile app market is saturated and there is a lot of competition.
What is the most interesting channel for you?
European strategic partners are generally the most promising market entry channel for providers like you. Selecting a channel depends on your type of company, the nature of your service, your target market, and the available resources for market entry. Regardless of the channel you choose, your own marketing and promotion is a vital part of your market entry strategy, for which you are responsible.
Tip:
- Decide on a business model. You can try to work directly for European end-users or focus on becoming a subcontractor for European partners. You should also create your ideal client persona. It helps you to tailor your offer.
3. What competition do you face on the European mobile application development services market?
There is a lot of competition in the mobile app development services market. In addition to competition on price and quality, there is also competition based on location. European “end-user” companies generally prefer outsourcing to providers within their country. Especially smaller ‘end-user’ companies outsource IT tasks locally. However, European ITO providers often subcontract to nearshore and offshore outsourcing companies. They usually prefer nearshore locations because of proximity, language, cultural similarities, and the minimal time difference.
Which countries are you competing with?
As European companies tend to favour outsourcing to nearshore locations, you primarily compete with providers from Europe, particularly those in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE) and Ukraine. These countries have numerous tech hubs, a highly skilled workforce, lower costs compared to Northern and Western European markets, good English proficiency, minimal time differences, and cultural similarities. In addition, you face competition from the major offshore ITO powerhouse India. The Philippines is also an important player.
The Global Services Location Index (GSLI) shows countries’ attractiveness as an offshore location for ITO/BPO services. It ranks their competitiveness based on 4 categories:
- Financial attractiveness;
- People skills and availability;
- Business environment;
- Digital resonance.
Based on the GSLI, India is the most attractive ITO/BPO destination. The Philippines also has a relatively high position, ranking 12th. CEE countries and Ukraine score lower but are leading outsourcing locations for European companies.
Source: Kearney, 2023
CEE countries: Preferred nearshoring destinations
European ITO providers often subcontract to nearshore destinations in CEE. Companies from these countries are viewed positively in the European market. They are often considered reliable. CEE countries are important outsourcing hotspots due to their skilled talent and geographic and cultural proximity to Northern and Western Europe. Poland and Romania are particularly large suppliers. Both have large pools of IT professionals. Being part of the EU means these countries have advantages in terms of legal compliance. They also have easier business integration when serving European clients.
Poland is the most attractive destination. It ranked 13th on the GSLI 2023. It has many higher education institutions, including 40 state universities and 20 public technology institutes. They have trained around 400,000 IT specialists. Polish IT specialists have experience working with international companies and are skilled in advanced technologies. The HackerRank shows that Poland’s programmers are amongst the best in the world. Poland is a large market with a relatively large economy for app-related jobs. In 2021, there were 121,000 app-related jobs.
Poland’s strong IT infrastructure and supportive government policies create an attractive business environment. The country draws a lot of foreign investments too. Global companies have invested billions of dollars in the Polish Digital Valley, new data centres, and expansions to Polish offices. The main IT hubs in Poland are Warsaw, Krakow, and Wroclaw.
Romania is another strong nearshore destination. Romania holds the leading position in Europe and is the 6th country worldwide for certified IT specialists per 1,000 inhabitants. The country has a large tech workforce of 120,000 programmers and more than 360 custom software development companies. Around 25,000 students (7% of all applicants) enrol in computer science programmes across nearly 100 universities and higher education institutions every year.
Romanian IT professionals have experience in foundational programming languages like Java, JavaScript, and C#. They also work with modern frameworks like React and Angular. Romania ranks highly on the English proficiency index as English is the primary working language amongst Romanian tech companies. Romania is known for its exceptional price-to-quality ratio.
Bucharest is the country’s main IT hub, holding 63% of the country’s software development revenues. IT companies in Bucharest serve the finance, e-commerce, healthcare, business services sectors, and more. Other IT hubs include Cluj-Napoca, Timișoara and Iași.
CEE countries face challenging with rising costs and talent shortages. The success of the tech sector has driven up talent competition and salaries in major hubs. The increased rates have narrowed the cost gap with Western Europe. Being in the EU also means businesses face higher operating costs than some offshore locations. As a result, some CEE companies subcontract work to offshore destinations. Although companies from CEE countries are your competitors, they also offer opportunities for partnerships.
India: Low-cost destination, mostly known for ‘bulk’ projects
India continues to lead the GLSI with its combination of low-cost services, high English proficiency, and a skilled workforce. This makes it a strong competitor in the IT outsourcing market. India has a young and fast-growing workforce. To stay ahead, the country must transition from lower-skilled jobs that can be replaced by robots to more creative and high-skilled work. Technological advancements and socioeconomic changes will reduce India’s labour cost advantage. This applies to other low-cost countries as well.
India is usually regarded as a ‘bulk’ destination. Buyers often associate extremely low developer rates in Asian countries with poorer project quality. They assume that cheap service providers must be using less skilled or less experienced developers, or that working conditions must be poorer.
India has a massive talent pool in terms of mobile app development. According to the Progressive Policy Institute (PPI), India had almost 1.7 million app economy jobs in 2019. So, the actual number at the time of writing is even higher. The cities with the most app-related jobs are Bangalore, New Delhi, Mumbai, Hyderabad, Pune, and Chennai.
Ukraine: A resilient tech industry
The technology sector is an important pillar of Ukraine’s economy, ranking 2nd in exports and contributing 4.4% to the country’s gross domestic product (GDP). According to the IT Research Ukraine 2024 report, Ukraine has 2,118 tech companies. About half of them provide services. Of these, 47% are focused on outsourcing and 3% on out-staffing. Most of the service companies are located in Kyiv, followed by Lviv and Kharkiv.
Quite a lot of Ukrainian tech companies are opening new offices abroad. The IT Research Ukraine 2024 report states that 51% of Ukrainian CEO’s want to expand their businesses. Of these, more than a third want to establish branches abroad. Poland is the preferred choice for expansion.
Ukraine has 302,000 professionals in the tech industry. Of these, 238,000 work within the country. 44.2% work in service companies. The country has a large pool of skilled tech talent. 43% of tech specialists have more than 6 years of experience. More than 82% of tech workers hold middle, senior, or lead positions. The average salary for a tech specialist is US$2,590.
The most popular software development areas in Ukrainian IT are backend (40.5%), frontend (22.7%), full stack (21.4%), and mobile (9.6%). In terms of the mobile category, the most popular programming languages are Kotlin and Swift. This is followed by Dart, TypeScript, and JavaScript. When it comes to the platforms Ukrainian IT companies develop for, 8.9% focus on Android, 8.4% on cross-platform development, and 8.3% on iOS.
Despite the war, around 85% of the Ukrainian developers have managed to keep working, either in Ukraine or abroad. Outsourcing software companies have taken several measures to continue business during the war such as relocating employees to safer areas, diversifying talent recruitment globally, independent internet solutions, and installing generators in offices.
The Philippines: English proficiency and cultural compatibility
The Philippines ranks 12th in the GSLI 2023. It is known for being a strong business process outsourcing (BPO) destination in Asia. However, its IT outsourcing sector is also developing quickly.
Its strong English proficiency is one of the Philippines' greatest strengths. The country ranks 22nd on the EF English Proficiency Index. Another strength is its cultural compatibility. Filipinos are familiar with Western norms. This makes it easier to conduct business and collaborate on projects in teams.
The Philippines has a large pool of IT graduates every year. But the talent pool for very advanced or specialised software developers is smaller than for example Ukraine and India. Worldwide, the Philippines ranks 46th in terms of the quality of its software developers. As a result, the Philippines might be a better fit for simpler mobile app development projects. Another disadvantage is the time zone. Due to the time difference with Europe, real-time collaboration is limited.
Tips:
- As many European buyers prefer to work with nearshore suppliers, be ready to answer questions about why they should choose your company over nearshoring options. For more information, see our tips on doing business with European buyers.
- To stand out from other countries and minimise competition, specialise in targeted horizontal, vertical, or niche segments.
Which companies are you competing with?
Examples of mobile app development companies include the following:
Brights (Poland)
Brights is a software development company with offices in Warsaw (Poland) and Kyiv (Ukraine). They serve clients in the UK and the United States. Their services include mobile app development, including both native apps (iOS and Android) and cross-platform solutions that use React Native. The company is active in a wide variety of sectors. For example, they create banking, insurance, augmented reality, and mobile marketplaces apps.
RipenApps (India)
RipenApps is a mobile and web app development company based in India. It has offices in multiple countries, including the UK. It is a medium-sized firm, but offers a wide variety of mobile app services. The company develops Android and iOS apps, and it uses frameworks like React Native, Flutter and Ionic for cross-platform app development. RipenApps also incorporates cutting-edge technologies in their app development process. This includes AI-powered solutions such as machine learning (ML), deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP).
Devlight (Ukraine)
Devlight is a Ukrainian IT company that specialises in mobile app development. The company’s vision is to transform companies into mobile-first businesses. The company serves various sectors, including neobank and fintech, healthcare, logistics, retail and e-commerce. Besides Ukraine, the company also holds offices in Warsaw (Poland), Tallinn (Estonia), and London (UK).
Exist (Philippines)
Exist is a company in Manila with over 100 employees. It offers multiple services such as software development, mobile app development, cloud services and UX design. It uses different kinds of technologies to develop mobile apps, such as Swift for iOS, Kotlin for Android, and Flutter for cross-platform developments. It specialises in 4 sectors: banking and finance, retail, healthcare, and energy.
Tip:
- Learn from your competitors. Look for competitors that operate in the European market. Compare them in terms of price, their offer, the segments, the industries they focus on and so on.
Which products are you competing with?
Unless you sell your own mobile application products to the European market directly, your service is your product: mobile application development services. So, the real question is: what makes one service provider different from another? There are a lot of answers. Providers differ in terms of aspects like technical and domain knowledge, capacity, references, flexibility, reliability, communication and language skills, quality management, security infrastructure, (niche) market focus, user-centric design, UX and more.
Mobile application development, as with any software development, involves many activities in the software development lifecycle (SDLC). They might also require software updates, routine maintenance, documentation and the development and implementation of new features. If you can take care of these tasks (so your clients can focus on their core business), this will make you stand out from your competition. Standing out from the competition is the result of providing a great user experience, strong performance, reliability and securely handling user data.
There is space in the market for innovation and developing your own mobile application product. However, it is a challenging, saturated market.
Tip:
- Look at mobile app development companies that have successfully entered the European market. Look at how they position and promote themselves in the European market. Determine how your company can get a competitive advantage by looking at factors like quality, cost, tech stack, and niche market focus.
4. What are the prices of mobile application development services on the European market?
Price is important, but it is not the main thing European buyers of mobile app development services look at. If they choose a provider from a developing country, they find communication and skills much more important than low prices. Nevertheless, your price must be right and competitive. The biggest price component in any project will be person-hours.
The price is influenced by:
- Technological requirements;
- Skill levels;
- Project complexity;
- Length of the contract;
- Other requirements in the Service Level Agreement (SLA) such as design complexity (UI/UX), backend development, third party integration, and security features.
Your quote should include the price, with a professional estimation of the project size. You should work out your pricing strategy for internal use. This includes:
- The pricing model you want to apply, such as Fixed-Price, Time and Materials, Incentive Based, or Shared Risk-Reward;
- Special pricing options (such as market penetration pricing);
- Price ranges for every job category, experience level, platform specialisation, and so on;
- Average price range of past projects;
- Project size expectations, minimum project size;
- Trial project conditions;
- Discount policy;
- Factors that may increase or decrease your price like a 24-hour work cycle, specific SLA agreements;
- Payment terms and expectations.
Salaries make up a large part of the costs in mobile app development. They vary depending on factors like years of experience, type of platform, and the country/city where the app developer is located. Some examples of salaries in different countries are given below.
- France: The median annual salary for an iOS and Android developer is €49,500, while cross-platform developers earn €51,250 per year. Junior app developer earn between €28,000 and €45,000 per year. Senior app developers earn between €40,000 and €95,000 per year.
- Germany: Junior Android developers earn a median salary of €52,500 per year and senior Android developers earn €70,000 per year.
- Poland: The median annual salary for an Android developer ranges from €23,000 (junior developer) to €62,000 (senior developer).
- India: The annual median salary for an app developer in India ranges from €6,000 (junior developer) to €17,000 (senior developer).
Outsourcing to countries where wages are lower can lead to considerable cost savings. If you focus on a niche or non-commodity market, European buyers are often less sensitive to price.
Tips:
- Study average prices, using IT Jobs Watch for example. You can also research average salaries using platforms like Payscale or Glassdoor.
- Analyse your costs and profit expectations to determine the right price for your services.
Globally Cool carried out this study in partnership with Laszlo Klucs on behalf of CBI.
Please review our market information disclaimer.
Search
Enter search terms to find market research